In “Understanding the Age Gap in U.S. Seniors,” we explore an intriguing aspect of retirement that is often overlooked – the age gap among seniors in the United States. Underneath the seemingly homogeneous category of “seniors” lies a wide range of individuals with varying life experiences, needs, and aspirations. This article sheds light on the complexities of aging, highlighting the importance of understanding the age gap among U.S. seniors and the implications it has on their lifestyles and well-being.
This image is property of www.prb.org.
Defining the Age Gap in U.S. Seniors
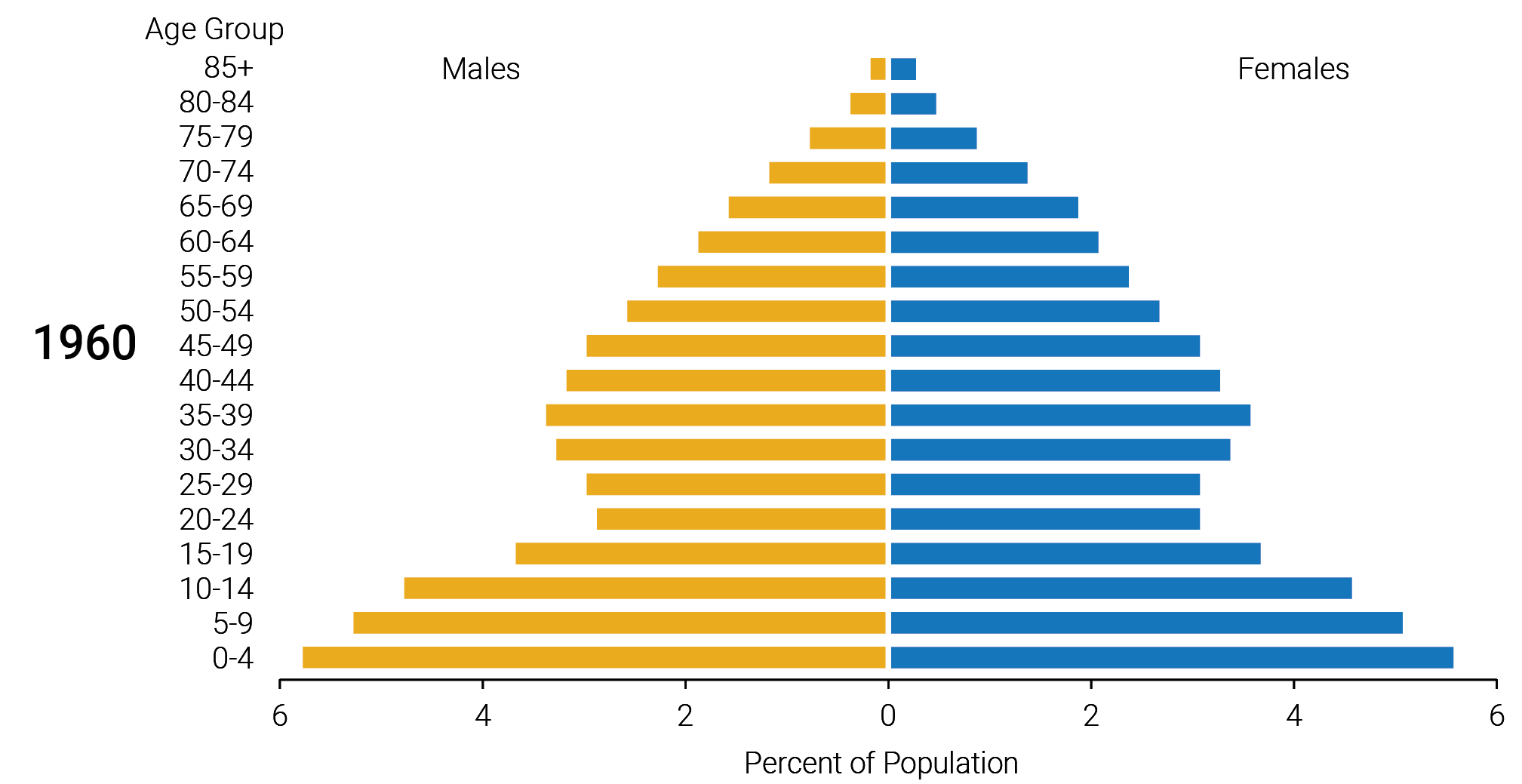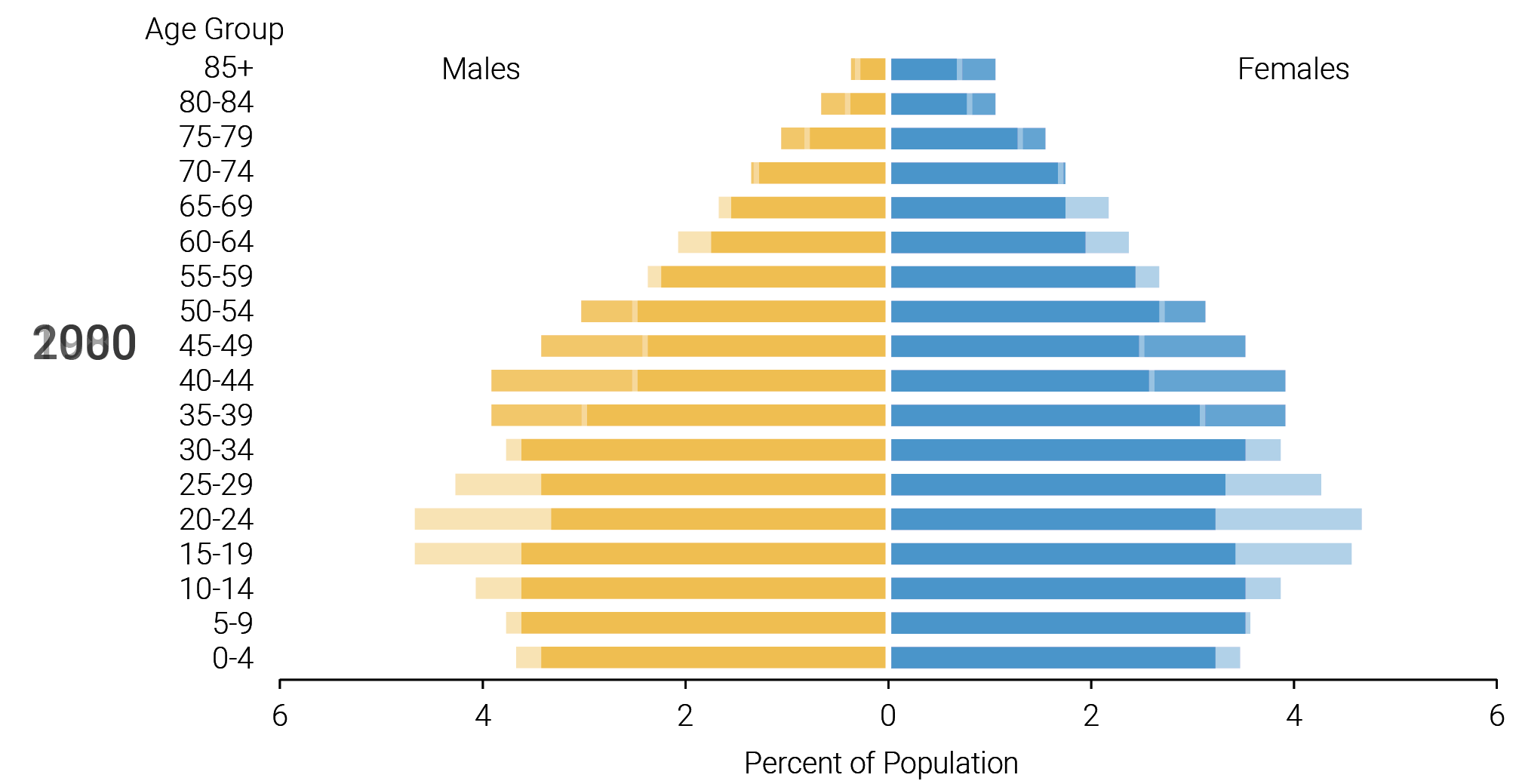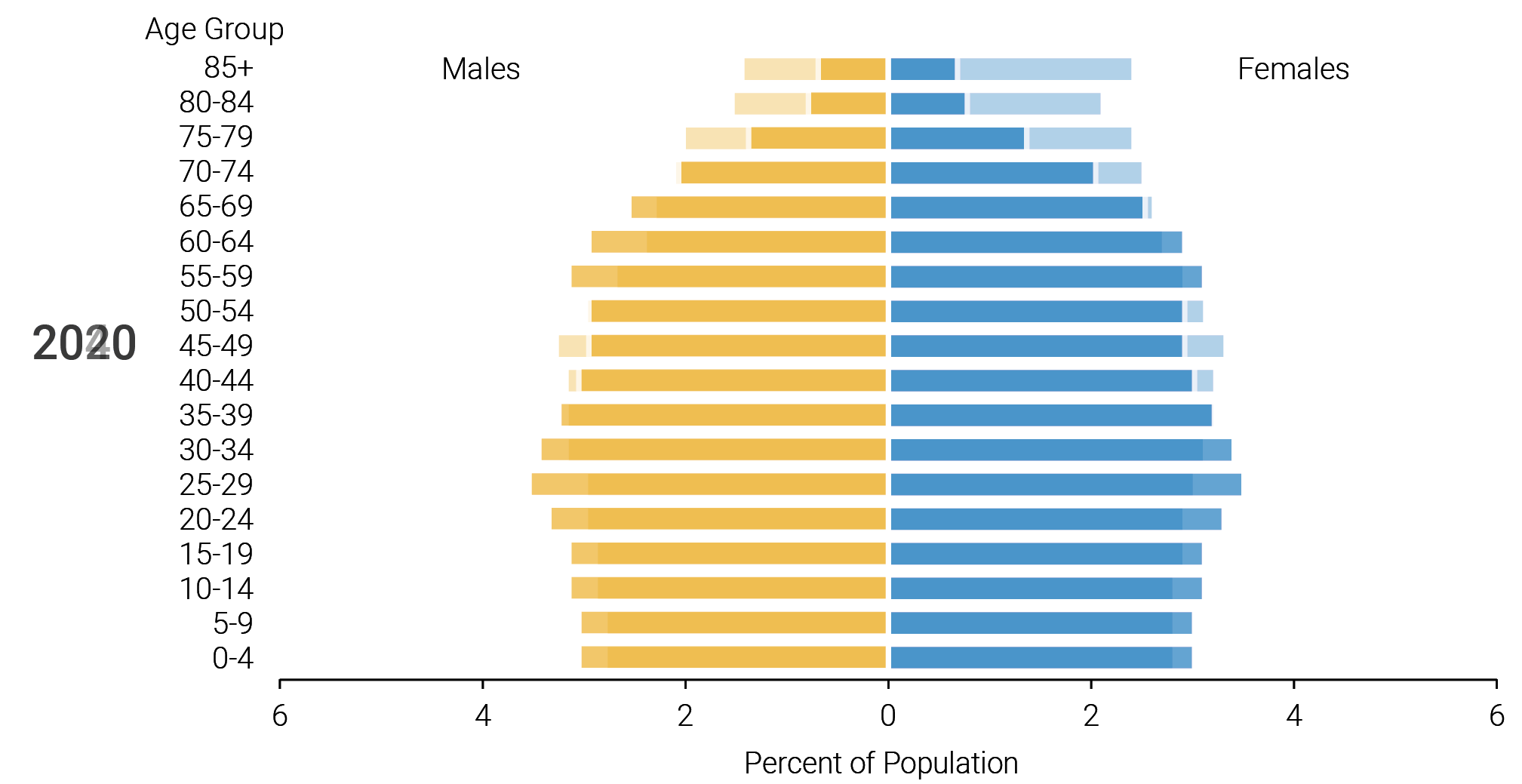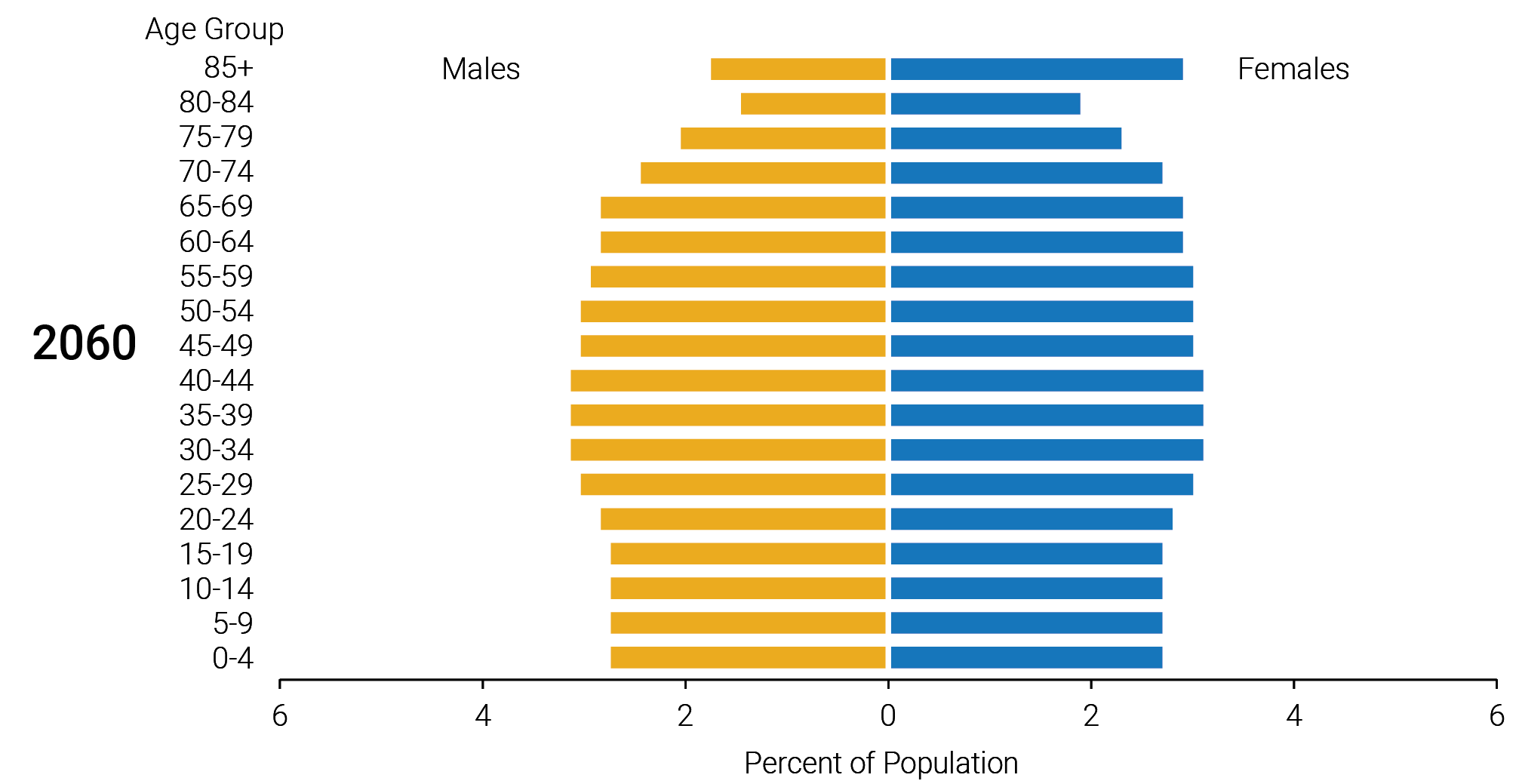
The age range of seniors in the U.S.
When it comes to defining the age gap among U.S. seniors, it is important to first understand the age range that qualifies individuals as seniors. In general, seniors are typically considered to be individuals who are 65 years of age or older. However, this age range may vary depending on different factors such as specific programs, benefits, or policies. For example, some programs or services may consider individuals as seniors once they reach the age of 60, while others may have a higher threshold of 70. It is important to keep in mind that the age range of seniors can have significant implications for healthcare, retirement benefits, and societal perception of aging.
Factors that contribute to the age gap among seniors
Several factors contribute to the age gap among seniors in the U.S. One major factor is the varying life expectancies among different demographic groups. Certain populations may have higher life expectancies, resulting in older individuals being classified as seniors. Additionally, socioeconomic factors, such as income and education, can also affect the age gap among seniors. Higher-income individuals may have access to better healthcare and resources that contribute to longer lifespans, while lower-income individuals may face barriers to healthcare and experience shorter life expectancies. Furthermore, cultural attitudes towards retirement and aging also influence the age gap. Some cultures may have different retirement ages or expectations for seniors, resulting in variations among different ethnic groups.
Variations within different senior demographics
It is important to recognize that the age gap among seniors is not uniform across all demographic groups. Within different senior demographics, there may be variations in terms of age, health, economic status, and cultural backgrounds. For instance, individuals from different ethnic backgrounds may have different life expectancies, leading to variations in the age gap within these groups. Additionally, factors such as access to healthcare services, educational attainment, and income disparities can further contribute to variations within different senior demographics. Understanding these variations is crucial for policymakers and organizations aiming to address the needs and challenges faced by seniors across different groups. By recognizing the unique characteristics and diverse needs of different senior demographics, more targeted and effective solutions can be developed to bridge the age gap among U.S. seniors.
Understanding the Retirement Age
The traditional retirement age in the U.S.
Traditionally, the retirement age in the U.S. was set at 65. This age was established as the standard retirement age when Social Security was first introduced in 1935. At that time, life expectancies were significantly lower, and most individuals did not live long beyond their retirement age. Therefore, 65 was considered an appropriate age to retire and begin receiving retirement benefits. However, as life expectancies have increased over the years, the traditional retirement age is being reevaluated.
Factors affecting retirement age
Various factors can influence an individual’s retirement age. One primary factor is financial stability. Many individuals choose to retire once they have accumulated enough savings and retirement funds to sustain their desired standard of living. Others may continue working due to financial constraints or the need to support dependents. Additionally, individuals in physically demanding professions may retire earlier due to health concerns or their inability to continue performing their job duties. On the other hand, those in less physically demanding occupations may choose to extend their working years if they enjoy their work or find it fulfilling.
Shifts in retirement age trends over time
In recent years, there has been a noticeable shift in retirement age trends. With increasing life expectancies and changing economic conditions, more individuals are choosing to delay retirement. Some do so to ensure financial security, while others may continue working to maintain mental and social engagement. Additionally, changes in Social Security policies have also influenced retirement age trends. Currently, the full retirement age for Social Security benefits is gradually increasing from 65 to 67, based on year of birth. This change is intended to address the financial strain on the Social Security system caused by the aging population.
Health and Life Expectancy of U.S. Seniors
Life expectancy trends among U.S. seniors
Life expectancy among U.S. seniors has been steadily increasing over the years. Advances in healthcare, improvements in living conditions, and better access to essential resources have all contributed to longer lifespans. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), the overall life expectancy for individuals aged 65 in the U.S. is approximately 19.5 years. However, it is important to note that life expectancy can vary significantly based on various factors such as gender, ethnicity, socioeconomic status, and access to healthcare.
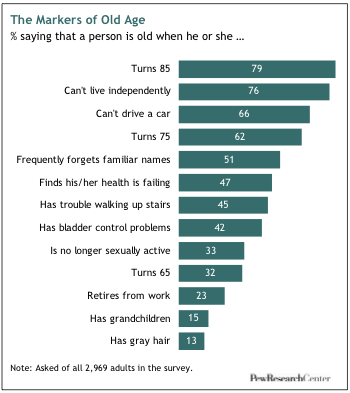
The impact of health on the age gap among seniors
Health plays a crucial role in the age gap among seniors. Individuals who experience good health and are able to maintain an active lifestyle may continue to work or engage in other productive activities well into their senior years. On the other hand, those who face health challenges or chronic conditions may be forced to retire earlier or experience limitations in their daily lives. These variations in health can contribute to a wider age gap among seniors, with some individuals enjoying robust health and remaining active well into their 70s and 80s, while others may require additional support and care at a younger age.
Changing perceptions of aging and its relation to life expectancy
Perceptions of aging have also evolved over time, with a growing emphasis on active and healthy aging. As life expectancies have increased, so too have societal expectations. More individuals are recognizing the potential for continued personal growth and contribution to society well into their senior years. Aging is no longer solely associated with decline and dependency but is increasingly viewed as a stage of life filled with opportunities and possibilities. This shift in perception has important implications for the age gap among seniors, as it encourages individuals to continue pursuing their passions and goals beyond traditional retirement ages.
Social and Economic Factors
Socioeconomic disparities among seniors
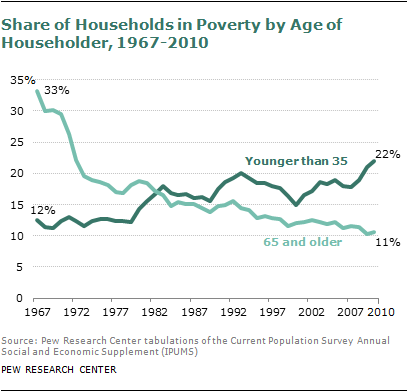
Socioeconomic disparities among seniors contribute significantly to the age gap. Higher-income individuals tend to have better access to healthcare, resources, and opportunities for lifelong learning, which can positively impact their overall well-being and life expectancies. Conversely, lower-income individuals may face challenges such as limited access to healthcare services, inadequate retirement savings, and increased stressors that can negatively affect their health and lifespan. These socioeconomic disparities perpetuate the age gap among seniors, as individuals from disadvantaged backgrounds are more likely to experience poorer health outcomes and shorter lifespans.
Relationship between educational attainment and age gap
Educational attainment also plays a role in the age gap among seniors. Research has consistently shown a positive correlation between higher levels of education and longer lifespans. Individuals with higher educational attainment tend to have better access to job opportunities, higher incomes, and healthier lifestyles. Additionally, education equips individuals with knowledge and skills necessary to make informed decisions about healthcare, retirement planning, and overall well-being. By addressing educational disparities and promoting equal access to education, the age gap among seniors can be reduced, leading to a more equitable and inclusive society.
Income disparities and their influence on the age gap
Income disparities significantly contribute to the age gap among seniors. Individuals with higher incomes often have more financial security, enabling them to access better healthcare services, afford healthier lifestyles, and save for retirement. On the other hand, lower-income individuals may struggle to meet their basic needs, face limited or no access to healthcare, and experience financial stress as they age. These income disparities can result in significant differences in health outcomes and life expectancies, widening the age gap among seniors.
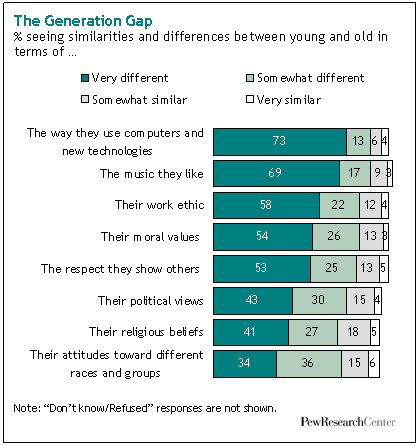
This image is property of www.pewresearch.org.
Regional Disparities in Senior Population
Variations in senior population by state
There are notable regional disparities in the senior population across different states in the U.S. Factors such as migration patterns, local economies, and access to healthcare services can contribute to these variations. Some states may have a higher proportion of seniors due to retirement destinations or cultural preferences, while others may have a younger population due to economic opportunities or limited healthcare access for seniors. Understanding these variations is important, as it allows policymakers to address specific needs and challenges faced by seniors in different regions.
Rural vs. urban divide and its impact on the age gap
The rural-urban divide also influences the age gap among seniors. Rural areas often have a higher proportion of seniors compared to urban areas. This can be attributed to several factors, including the migration of younger individuals to urban centers for job opportunities and limited access to healthcare services in rural areas. Rural seniors may face unique challenges such as limited transportation options, fewer healthcare providers, and reduced access to social activities. These challenges can impact their overall well-being and contribute to a wider age gap in rural communities.
Regional factors influencing the age gap among seniors
Regional factors such as climate, economic conditions, and cultural attitudes towards aging and retirement can influence the age gap among seniors. For example, regions with harsher climates may have shorter life expectancies due to increased health risks associated with extreme weather conditions. Additionally, economic conditions can impact retirement savings and access to resources, affecting the well-being and life expectancy of seniors. Cultural attitudes towards aging and retirement can also vary across regions, leading to variations in the age gap. Understanding and addressing these regional factors is crucial for developing targeted strategies to reduce the age gap among seniors.
Ethnic and Cultural Influences
Differences in life expectancy among different ethnic groups
Life expectancy varies across different ethnic groups in the U.S. Factors such as socioeconomic status, access to healthcare, cultural practices, and genetic factors contribute to these differences. Research has consistently shown that certain ethnic groups tend to have longer life expectancies compared to others. For example, Asian Americans and Hispanic Americans generally have higher life expectancies compared to non-Hispanic white Americans and African Americans. These variations in life expectancy among different ethnic groups can contribute to the age gap among seniors.
Cultural attitudes towards retirement and aging
Cultural attitudes towards retirement and aging also play a significant role in the age gap among seniors. Different cultures may have varying expectations and traditions regarding retirement. Some cultures prioritize familial support and intergenerational living arrangements, which can delay the retirement age for individuals within these cultural groups. On the other hand, cultures that emphasize individual independence and personal achievement may have different retirement demographics. Understanding and respecting cultural attitudes towards retirement is crucial for addressing the needs and challenges faced by seniors from diverse ethnic backgrounds.
Effect of ethnic diversity on the age gap in U.S. seniors
The ethnic diversity of the U.S. population contributes to the age gap among seniors. As the population becomes increasingly diverse, it is important to recognize and address the unique needs and challenges faced by different ethnic groups. Ethnic diversity brings with it a range of cultural perspectives and practices that influence retirement decisions, health outcomes, and overall well-being. By promoting inclusivity and understanding the impact of ethnic diversity on the age gap, policymakers can develop policies and programs that cater to the diverse needs of U.S. seniors.
This image is property of www.pewresearch.org.
Gender Disparities
Gender distribution among U.S. seniors
The gender distribution among U.S. seniors is not equal, with women comprising a larger proportion of the senior population. This is partly due to longer life expectancies among women compared to men. Women tend to live longer than men, resulting in a higher number of senior women in the population. Additionally, historical factors such as higher mortality rates among men during wars and workplace hazards have contributed to the gender disparity among seniors.
Factors contributing to gender differences in the age gap
Several factors contribute to the gender differences in the age gap among seniors. Biological and genetic factors play a role, with women generally having a longer life expectancy. However, social and cultural factors also influence the age gap. Women tend to have different experiences throughout their lives, such as child-rearing responsibilities, career interruptions, and disparities in earning potential. These factors can impact retirement savings, access to healthcare, and overall well-being, resulting in variations in the age gap between men and women.
Societal expectations and their role in gender disparities
Societal expectations and norms also contribute to gender disparities in the age gap among seniors. Historically, women were expected to assume caregiving roles and prioritize familial responsibilities over their own careers and personal well-being. These societal expectations may have limited women’s opportunities for career development, retirement savings, and access to resources. Consequently, women may face higher levels of financial insecurity and healthcare challenges in their senior years, widening the age gap between genders.
Social Security and Retirement Benefits
The role of Social Security in bridging the age gap
Social Security plays a crucial role in bridging the age gap among U.S. seniors. Social Security benefits provide income support for retired individuals, helping to alleviate financial burdens and ensure a basic standard of living. By providing a reliable source of income, Social Security allows seniors to meet their healthcare needs, cover daily expenses, and maintain a reasonable quality of life. However, the effectiveness of Social Security in bridging the age gap depends on various factors, including the adequacy of benefit amounts, eligibility criteria, and the overall financial stability of the program.
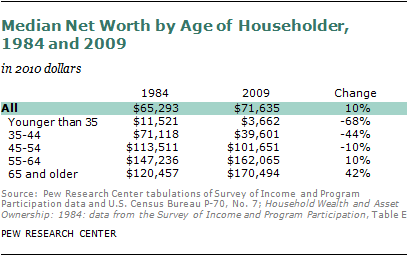
Variations in retirement benefits among seniors
Retirement benefits can vary significantly among seniors based on various factors. Social Security benefits are calculated based on an individual’s earnings history and the age at which they choose to retire. Early retirement, before the full retirement age, results in reduced monthly benefit amounts, while delaying retirement can lead to increased benefits. Additionally, pension plans and employer-provided retirement benefits also differ among individuals based on career choices, employer policies, and other factors. It is important for individuals to understand their retirement benefits and plan accordingly to bridge the age gap effectively.
The impact of retirement benefits on the age gap
Retirement benefits have a direct impact on the age gap among seniors. Adequate and reliable retirement benefits enable individuals to retire comfortably and maintain financial security throughout their senior years. On the other hand, limited or insufficient retirement benefits can lead to financial strain, increased reliance on social programs, and ongoing work beyond traditional retirement ages. By ensuring the availability of comprehensive retirement benefits, the age gap among seniors can be reduced, allowing individuals to retire with dignity and enjoy their golden years.
This image is property of www.pewresearch.org.
Healthcare and Aging
Access to healthcare services for seniors
Access to healthcare services is a critical factor in bridging the age gap among seniors. Older individuals often require more comprehensive and specialized medical care to address age-related health concerns. However, healthcare access can vary among seniors based on factors such as location, income, insurance coverage, and availability of healthcare providers. Rural areas, in particular, may face challenges due to limited healthcare facilities and long distances to medical centers. Ensuring equitable access to healthcare services is essential for addressing the age gap among seniors and promoting overall well-being.
Healthcare costs and their influence on the age gap
Healthcare costs significantly influence the age gap among seniors. As individuals age, healthcare expenses tend to increase due to the need for ongoing medical care, prescription medications, and long-term care services. High healthcare costs can create barriers to accessing essential services, medication, and preventive care, particularly for individuals with limited financial resources. Age-related conditions and chronic illnesses can further exacerbate healthcare expenses, widening the age gap among seniors. Affordable healthcare options and assistance programs are vital for reducing the financial burden on seniors and ensuring that they receive the care they need.
Advancements in healthcare and their impact on aging
Advancements in healthcare have had a profound impact on aging and the age gap among seniors. Medical breakthroughs, improved diagnostic tools, and innovative treatments have contributed to longer and healthier lives for many individuals. These advancements have allowed seniors to manage chronic conditions, address age-related health concerns, and lead active lives well into their senior years. However, it is important to ensure that these advancements are accessible to all seniors, regardless of their socioeconomic status or background. By embracing and expanding upon healthcare innovations, the age gap among seniors can be further reduced, leading to a more inclusive and healthy aging population.
Future Implications and Solutions
Projected changes in the age gap among U.S. seniors
Looking toward the future, the age gap among U.S. seniors is projected to undergo further changes. With advancements in healthcare, improvements in living conditions, and evolving societal perceptions of aging, life expectancies are expected to continue rising. This trend may lead to a wider age gap among seniors, with a growing number of individuals enjoying longer, healthier lives. Additionally, demographic shifts, such as the aging baby boomer generation, will impact the senior population and contribute to changes in the age gap. It is essential for policymakers and organizations to adapt and plan accordingly to address the evolving needs and challenges associated with the age gap.
Potential strategies to reduce the age gap
To reduce the age gap among U.S. seniors, several strategies can be considered. Firstly, increasing access to affordable healthcare services, particularly in rural areas and underserved communities, is crucial. This can be achieved by improving healthcare infrastructure, expanding telehealth services, and implementing policies that promote healthcare affordability. Secondly, addressing socioeconomic disparities through initiatives that promote equal access to education, retirement savings plans, and financial literacy can help bridge the age gap. Additionally, programs and policies that support lifelong learning, skill development, and intergenerational activities can enhance quality of life, social engagement, and overall well-being for seniors. By implementing these strategies, the age gap among seniors can be reduced, leading to a more equitable and inclusive society.
The importance of understanding the age gap for policymakers
Understanding the age gap among U.S. seniors is crucial for policymakers in order to address the unique needs and challenges faced by this population. By recognizing and analyzing the factors contributing to the age gap, policymakers can develop targeted interventions, programs, and policies that promote a more equitable society. It is essential to address disparities in healthcare access, retirement benefits, socioeconomic factors, and cultural attitudes towards aging. By working collaboratively with stakeholders, policymakers can ensure that seniors have the opportunity to age with dignity, access necessary resources, and enjoy a high quality of life. By prioritizing the understanding and reduction of the age gap, policymakers can contribute to a future where every senior is valued and supported.
This image is property of www.pewresearch.org.